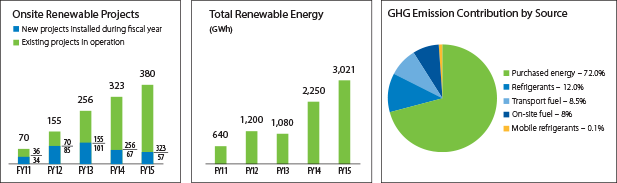
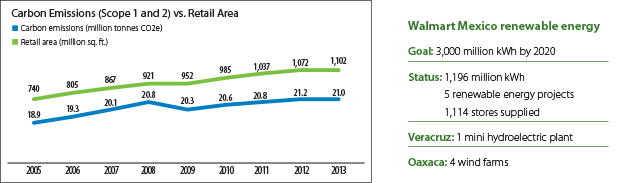
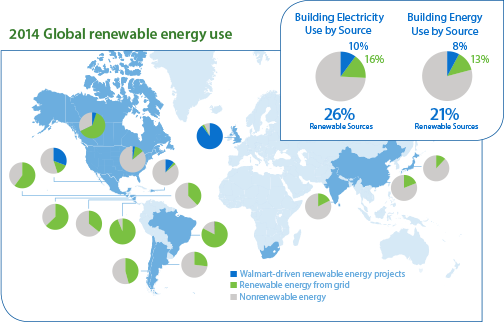
Doubling on-site solar
In May 2014, President Barack Obama visited our Mountain View, Calif., store to outline his plan for the U.S. to generate more clean energy. At that time, Walmart was already the No. 1 commercial solar energy user and the largest on-site renewable energy user in the U.S. But we supported the plan by committing to doubling the number of on-site solar energy projects at our U.S. stores, Sam’s Clubs and distribution centers by 2020, compared with our 2013 baseline. That’s more than 480 sites by 2020.
Our Mountain View store serves as one of several examples of that commitment at work. The facility currently generates 14.5 percent of its energy from solar systems built and installed by SolarCity, a local California business and one of our largest solar vendors. SolarCity estimates Walmart’s commitment to solar alone has created 9,000 construction jobs in the U.S. and led to the company’s adding 5,000 permanent American jobs since 2010. The commitment of Walmart and other companies to solar creates more certainty in the marketplace and encourages others to invest, which helps lower the cost for everyone.